Simulation learning is the process where trainees practise a procedure or routine in a simulated learning environment (SLE) before treating actual patients. These environments use different scenarios and equipment, and vary in realism.
Repeating the practice of simulated scenarios and actions in a controlled environment enables a realistic and flexible alternative to traditional clinical training methods, and aids in improved learning and knowledge gained from theoretical studies.
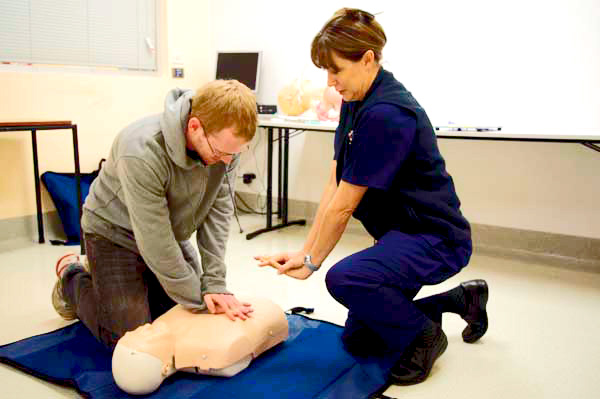
Low fidelity mannequin training
SLEs are classified into 3 levels of complexity – low, medium or high fidelity.
Low fidelity
Low fidelity simulations use strategies such as basic written case studies and/or role playing, e.g. simulated administration of injections.
Medium fidelity
Medium fidelity simulation involves the use of more realism, but without automatic cues such as the rise of the chest to simulate breathing. This type of simulation may involve the use of mannequin or actors trained to demonstrate a condition.
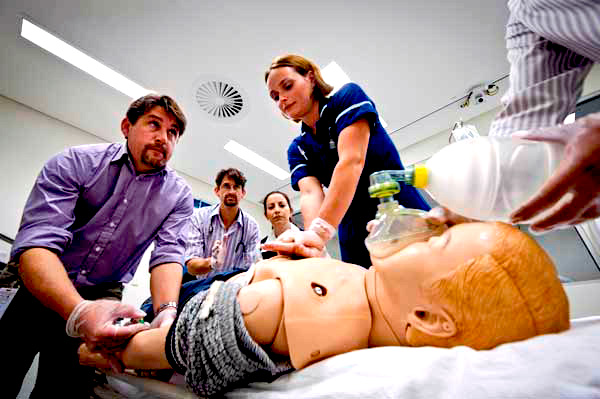
Medium fidelity mannequin training
Low and medium fidelity simulations are the most cost-effective, and usually focus on tasks and discrete situations. Most simulation learning takes place at these levels, using low-technology equipment.
These courses are most appropriately delivered in the hospitals where health professionals’ work, as learning can be tailored to meet the needs of the individual workplace.
High fidelity
High fidelity simulation provides the most realistic experience, primarily using computer-based mannequins, and may use cadavers or animal tissue.
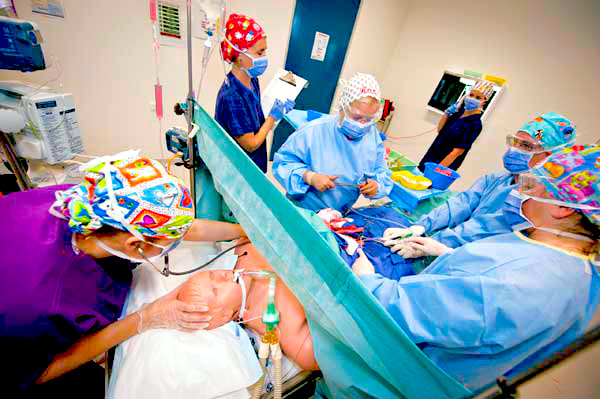
High fidelity mannequin training
These techniques are needed for situations that cannot be replicated safely using living patients or lower fidelity mannequins. They are used to teach advanced clinical skills, such as, surgery and anaesthetics.
More information
Department of Health
WA Clinical Support Network
Level 1 B Block, 189 Royal Street
East Perth WA 6004
Phone: 9222 2334
For general enquiries or join our mailing list email wactn@health.wa.gov.au